東洋医学
東洋医学
定義と歴史
東洋医学は、中国・日本・朝鮹半島など東アジアを起源とする伝統的医療体系の総称です。気・血・水(津液)や経絡(気の流れの道筋)、陰陽・五行など独自の理論で人体と自然の調和を図り、病気を身体全体のバランスの乱れと考えます。
2000年以上前の中国古典(黄帝内経など)を起源とし、日本へは奈良~平安時代に伝来。その後、鎌倉~江戸期に独自の発展を遂げ、明治以降は「漢方」や「鍼灸」を中心に近代化・体系化されました。
理論基盤
- 気・血・水(津液):生命活動を支える基本物質。
- 陰陽論:対立・制約する2つの性質(陰と陽)の調和が健康の要。
- 五行論:木・火・土・金・水の五つの要素で自然と人体を対応づけ、相生・相克関係で説明。
- 経絡(経筋・絡脈):気が流れるネットワークで、治療は経穴(ツボ)への刺激を通じて行う。
診断法
東洋医学の診断は「四診」に基づきます。
- 望診:顔色や舌の状態を観察
- 聞診:声や呼吸音、体臭を聴取
- 問診:症状・生活習慣・精神状態などを問う
- 切診:脈拍(脈診)、腹診・押圧による診察
これらを総合し、証候(パターン)を辨証論治のフレームで把握・治療方針を定めます。
主な治療法
- 漢方薬(煎じ薬・エキス製剤)
- 鍼(はり)・灸(きゅう)
- 推拿・按摩(中国式推拿、指圧やあん摩など日本流手技)
- 刺絡・刺血(皮膚微小出血による邪気排出)
- 薬膳・気功・導引(呼吸法・体操)
西洋医学との比較
西洋医学が病原体や臓器レベルの異常を直接的に診断・治療するのに対し、東洋医学は全身のバランス(気血水の循環や陰陽五行の調和)を重視し、自然治癒力の賦活を目指します。両者は相補的な関係にあり、現代では併用・統合(統合医療)の流れが加速しています。
現代の統合と規制
- 日本では1950年に日本東洋医学会が設立され、鍼灸・漢方薬は保険適用範囲が拡大。医師による漢方処方や鍼灸師の国家資格が確立しています。
- 世界的にはエビデンスを重視したRCTやメタ解析、オミクス解析による作用機序の解明が進行中。東洋医学の理論と現代生理学・分子生物学を橋渡しする研究が増えています。
東洋医学の奥深さは、単なる治療技術を超え、自然観・身体観を包括する思想体系にあります。次は、臨床応用における証拠レベルの整理や、現代分子基盤から経絡刺激が神経・免疫系へ与える影響について掘り下げてみましょう。
Integration of Eastern
and Western Medicine
Overview
Eastern and Western
medicine share the goal of promoting health and treating disease but differ in
philosophical frameworks and methods. Integrating both systems creates a
holistic model that leverages the precision and rapid intervention of Western
medicine alongside the preventive, balancing approaches of Eastern traditions .
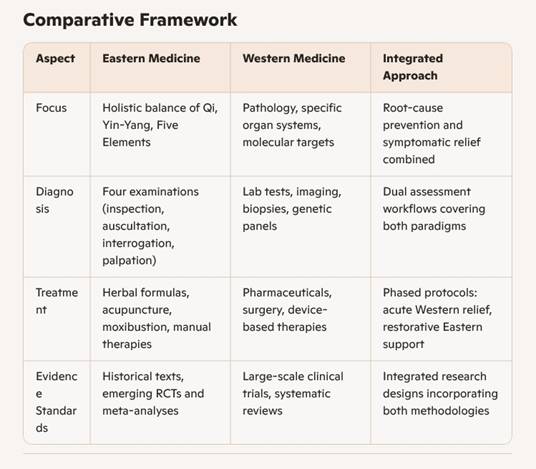
Philosophical Complementarity
- Eastern medicine views the body as an
interconnected whole, emphasizing balance among energy systems (Qi),
prevention, and the mind-body connection .
- Western medicine focuses on diagnosing
specific pathological processes through laboratory tests, imaging, and
targeted pharmacology or surgery .
- Integration aligns these perspectives by
addressing root causes and symptom relief in tandem, fostering both
immediate and long-term health.
Practical Models of
Integration
- Hospital and Clinic Settings
- Many Western
hospitals now offer acupuncture, herbal consultations, yoga classes, and
meditation alongside standard care .
- Pain clinics
combine NSAIDs or nerve blocks with acupuncture or Tuina massage for
enhanced relief in conditions like lower back pain and irritable bowel
syndrome .
- Multidisciplinary Teams
- Collaborative
networks bring together physicians, acupuncturists, naturopathic doctors,
and mind-body therapists.
- Regular case
reviews ensure cohesive treatment plans that respect drug-herb safety and
optimize timing and dosing of all interventions .
- Culturally Competent Care
- Integrating Eastern practices addresses
healthcare disparities by tailoring services to diverse cultural beliefs
and values .
- Staff training in cultural awareness and
linguistic competency enhances patient engagement and adherence.
Evidence Base and
Research
- Randomized controlled trials show
acupuncture adds benefit to conventional pain management protocols for
chronic low back pain.
- Meta-analyses suggest meditation and tai
chi improve mental health outcomes when used alongside
cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy.
- Omics approaches are now decoding how
acupuncture stimulation modulates immune markers and neural pathways, bridging
TCM theory and molecular physiology.
Comparative Framework
Case Example: Chronic Low Back Pain
- Phase 1 – Acute Relief
- Administer NSAIDs
or muscle relaxants and consider epidural injections.
- Begin gentle
acupuncture sessions to modulate nociceptive pathways and reduce
inflammation.
- Phase 2 – Restorative Care
- Introduce
moxibustion or Tuina massage for tissue repair and Qi regulation.
- Add tai chi or
guided meditation for stress reduction and core strengthening.
- Phase 3 – Preventive Maintenance
- Develop a personalized herbal regimen to
support musculoskeletal health.
- Schedule periodic mind-body classes to
sustain balance and prevent recurrence.
Benefits and Challenges
- Enhanced patient
satisfaction and adherence through culturally sensitive options.
- Synergistic effects
yield better outcomes in pain, stress, and chronic disease management.
- Broader therapeutic
toolbox reduces reliance on pharmaceuticals alone.
- Ensuring safety by monitoring herb-drug
interactions and standardizing quality of herbal products.
- Bridging regulatory frameworks for
credentialing practitioners across specialties.
- Designing rigorous trials that honor both
scientific and traditional evidence metrics.
Emerging Directions
- Molecular studies mapping acupuncture’s
impact on cytokine networks and central pain circuits.
- AI-driven integrative diagnostics
combining omics data with TCM pattern recognition.
- Development of hospital-based integrative
medicine fellowships to train the next generation of practitioners.
Additionally, exploring
regulatory pathways for herbal extracts in Japan can reveal strategies to
streamline approval and quality control. You might also consider how digital
health tools, like remote pulse diagnosis and virtual qigong classes, will
shape the future of integrative care.

